CalculatorTool¶
Calculations or logical queries can be performed with the CalculatorTool. In contrast to C# or VB scripts, no programming knowledge is required here.
Inputs
The inputs can be added as a terminal by dragging and dropping them onto the tool. The following data types are supported:
System.Int32
System.Double
System.Boolean
System.Int32[]
System.Double[]
System.VisionPro.CogToolResultConstant
Alternatively, inputs can be defined in the Tool Editor:
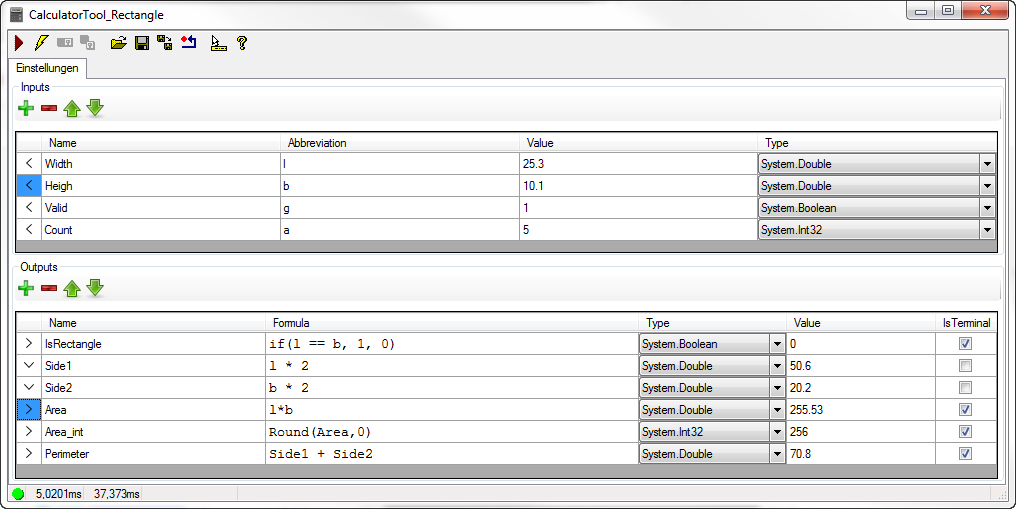
Plus symbol: Manually add an input terminal
Minus symbol: Remove the selected input terminal
Arrow up/down: Change sort order
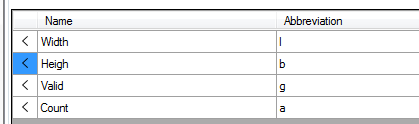
Name: Name of the input terminal
Abbreviation: Abbreviation of the name that can be used as an alternative to the name in the ouput formulas.
Value: Current value of the terminal
Type: Data type of the terminal
Outputs
The results of the tool are created under “Outputs”. Both intermediate results without an output terminal and final results with an output terminal can be defined.
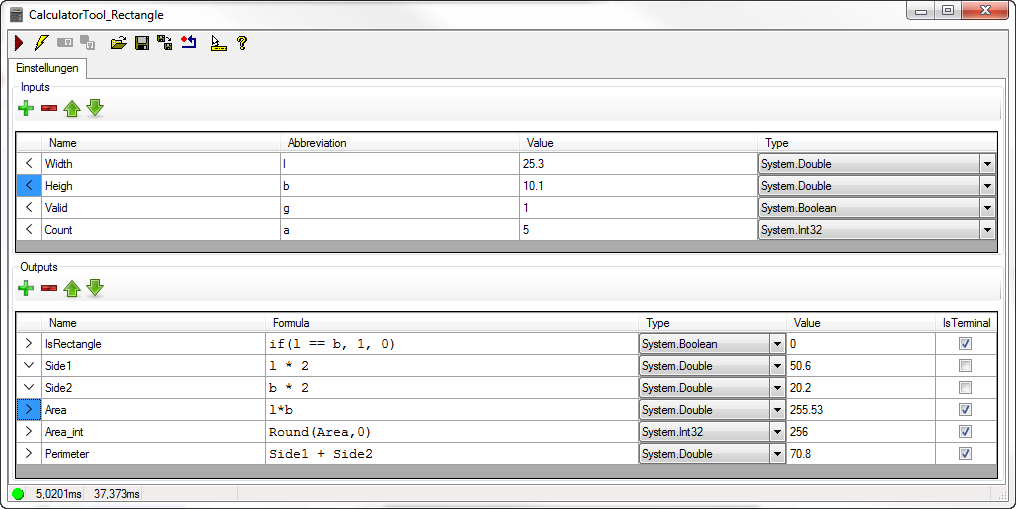
Plus symbol: Manually add an output
Minus symbol: Remove the selected output
Arrow up/down: Change the sort order.
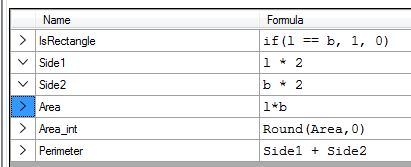
Name: Name of the output
Formula: Enter a formula for calculating the output value (see below).
Type: Data type of the output
Value: Current value of the output
IsTerminal: A terminal is to be created for the output.
Warning
The outputs are calculated in the sort order. When sorting, please note that intermediate results must be determined before the first use.
Enter the formula
The formulas for calculating the output values are specified in the “Formula” field. Via the context menu (right-click on the “Formula” field) all possible operators, constants and functions are listed and can be selected:
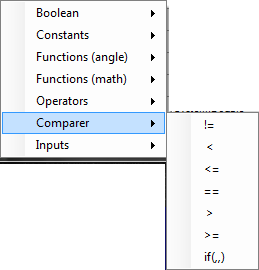
In addition, all inputs (with the name entered under “Abbreviation”) are available. Outputs calculated before the current value can also be used.
Example of inputs
Example of outputs
Hint
The decimal separator is a period in all fields.
Passing parameters of functions are separated with commas.
Spaces between operators are ignored.
Several functions can be nested within each other.
It is possible to convert between data types, i.e. to assign a different data type to an output than the expected result. It should be noted that, for example, when converting from double to integer, the decimal places are truncated and not rounded!
With an If condition, three parameters must be passed. The first represents the condition, the second the value if the condition is true and the third the value if the condition is not true.
Available Constants, Operators, Functions
Constant |
Description |
|---|---|
e |
Euler’s number |
pi |
circular number Pi |
In addition, all inputs (via the shortcut) and the outputs are available above the current entry.
Operator |
Description |
|---|---|
+ |
Add, positive sign |
- |
Subtract, negative sign |
( |
Open bracket |
) |
Closed bracket |
* |
Multiply |
/ |
Divide |
^ |
XOR operator |
!= |
Unbalanced |
< |
Small |
<= |
Smaller equal |
== |
Coming soon |
> |
Larger |
>= |
Greater equal |
if(,,) |
If-condition -> if(<condition>, <true>, <false>) |
Bool functions
Function |
Description |
|---|---|
and(,) |
Logical AND operator |
neg(,) |
Logically negate |
or(,) |
Logical OR operator |
xor(,) |
Logical XOR operator |
Angle functions
Function |
Description |
|---|---|
DegreeToRad() |
Convert angles to degrees to radians |
RadToDegree() |
Convert angles to radians to degrees |
RadToMinus45Plus45() |
Convert angles in radians to degrees and move them to the value range [-45°; 45°]. |
RadToMinus180Plus180() |
Convert angles in radians to degrees and move them to the value range [-180°; 180°]. |
RadToZero360() |
Convert angles in radians to degrees and move them to the value range [0°; 360°]. |
RadToZeroAngle(,) |
Convert angles in radians to degrees and move them to the value range [0°; <default>°]. |
RadToMinusAnglePlusAngle(,) |
Convert angles to radians to degrees and move to the value range [-<default>°; <default>°]. |
Mathematical functions
Function |
Description |
|---|---|
abs() |
Absolute value of a number, amount |
ceil() |
Round up |
cos() |
Cosine |
cosh() |
Cosine hyperbolic |
cot() |
Cotangens |
exp() |
Exponential function |
floor() |
Round up |
ln() |
natural logarithm |
log(,) |
Logarithm -> log(<number>, <base>) |
max(,) |
Maximum value of two numbers -> max(<number1>,<number2>) |
min(,) |
Minimum value of two numbers -> min(<number1>,<number2>) |
pow(,) |
Power calculation -> pow(<number>, <power>) |
round(,) |
Round a number -> round(<number>, <decimal places>) |
sin() |
Sync by honeybunny |
sinh() |
Sinus Hyperbolic |
sqrt() |
Root calculation |
tan() |
Tangent |
tanh() |
Tangent hyperbolic |